Best viewed using:
Internet Explorer
or
Mozilla Firefox
Connecting the N8047 Campfire / Fireplace Simulator
Installing the N8047 is very straightforward. Their tiny sizes and thin construction will allow them to be placed in many spaces too small for even the smallest Z-scale decoder. Because the module has circuitry on both sides, care must be taken to be sure that the components or wires soldered will not make contact with any metal object (such as a locomotive frame) causing a short circuit.
If the N8047 is to be used in a stationary (not track powered) application, it can also be powered by any well-filtered and regulated DC power source with an output of 6-18VDC. The N8047 with LEDs attached will draw only about 21ma of current so even the smallest DC power source (or a battery of sufficient voltage) should be adequate.
Included with the module are two 6” lengths of #32 insulated wire. If necessary, these can be used for power input wires.
If using this module in a DCC configured locomotive, most wired DCC decoders have a blue wire which is the common connection for all wired functions (F0, F1, etc.). It is the + DC connection and will be connected to solder point #1 as shown in Fig. 1.
If the decoder is a “drop-in” style without wires, consult the decoder manual and use the blue wire supplied to connect point #1 to the appropriate + solder pad.
![]()
Figure 1
If the solder pad has a resistor in series with it, be sure to connect the blue wire behind the resistor (see Fig. 2). This will ensure full voltage is supplied to the module.
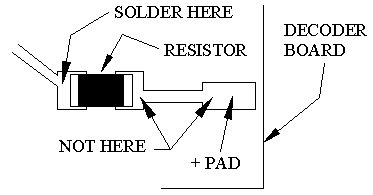
Important note: A low-wattage iron with a pointed tip should be used for connection of wires. Too much heat or solder can easily damage the wires, decoder or module and void the warranty.
Also, all connecting wires should be pre-tinned before soldering them to the module. This will make connection quick and easy and ensure excessive heat is not applied to the solder points.
Next, choose the function you want to control the N8047 module and connect the appropriate function wire to solder point #2. For example: If you want F1 to turn on the N8047/B connect the green wire to #2.
Again, if the decoder is the drop-in style, use the enclosed green wire to connect the appropriate function solder pad to #2. Make sure the pad chosen for this connection is not a “+” pad , but a function pad (– DC connection).
Whichever function you choose, make sure it is programmed for On/Off control only. Do not program the function for special effects. The N8047/B will control the special effects.
Direct Track powering (without a decoder connection)
All of our Simulators require a clean DC voltage of known polarity for their power source. Track power is typically provided in one of two forms. DC voltage (analog), or DCC.
Analog track power has been around for more than 75 years. Simply put, a DC voltage is applied to the two tracks with one being +DC and the other, -DC. Increase the voltage and the electric motor in the locomotive spins faster making the train go faster. If the train is required to reverse, track polarity is reversed so the loco's motor turns in reverse. Also, what defines "forward and reverse" is dependent on which way the loco is facing when it's put on the track. Bottom line here is that track polarity is not fixed. Our Simulator needs fixed polarity.
DCC track power is such that to devices requiring plain DC voltage, it looks like AC power. That is because voltage levels on each track go both + and – continuously. The DCC decoders in locomotives “descramble” the track signals and provide correct polarity so their motors can function normally. It is this process that will allow multiple locomotives to go in different directions on the same section of track, at the same time (a feature not available with analog track power). Once again, our Simulator needs fixed polarity and it needs to look like DC voltage.
Due to our Simulator's very small size, there is insufficient space to include additional circuitry and components necessary for proper power conditioning when direct track pickup is to be used. There are two solutions to this problem and both are inexpensive:
Discrete components
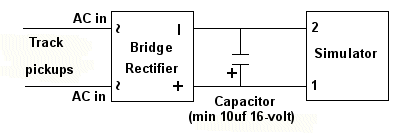
The Simulator can be powered from the track with the addition of two readily available components: a bridge rectifier (our N301S or N302S will work just fine). If DCC operation is used, the addition of a filter capacitor (10μf or larger and minimum 16-volt) will be required. Figure 3 below is schematic diagram of the connections required.
Figure 3
This is the least expensive solution, but is has a couple of minor drawbacks. First, the bridge rectifier (and capacitor, if needed) are not mounted on a circuit board so direct solder connection is required and you will need to ensure the pins on the rectifier and leads on the capacitor (depending on the type of capacitor) are organized so that they won't short out against anything. Second, depending on the physical size of the bridge selected (and capacitor, if needed) and the scale you're modeling, hiding these additional components so they're not noticeable can be a bit of a challenge.
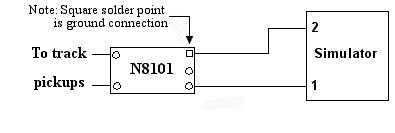
N8101 DC Power Source
A more elegant, but very slightly more costly ($3.95) solution would be to use our N8101 DC Power Source. It has all of the components needed, includes a circuit board with solder points, is extremely tiny (1/2 the size of our Simulator), has the lowest possible voltage loss (important for analog operators). Click here for more information on the N8101. Figure 4 below is schematic diagram of the connections required.
Figure 4
Connecting LEDs
When connecting the LEDs, proper polarity must be observed. LEDs are “polarity sensitive” and will not function is connected backwards. The N8047 is configured to connect either two 20 ma series-wired LEDs with device voltages of 2.0 VDC, or a single LED with a resistor (included with a spare in the package) in series with the LED. This covers all of Ngineering’s Micro and Nano yellow LEDs, as well as many of the yellow LEDs available.
Using wire appropriate for the size of the LED and its placement in the model, for a two LED application, connect the first LED anode (the + connection) to solder point 4. Connect the cathode (- connection) of this LED to the anode of the second LED and connect the cathode (- connection) of the second LED to solder point 3. For a single LED, substitute one of the included resistors for the second LED. Figure 5 (below) is a schematic diagram of the connections required.
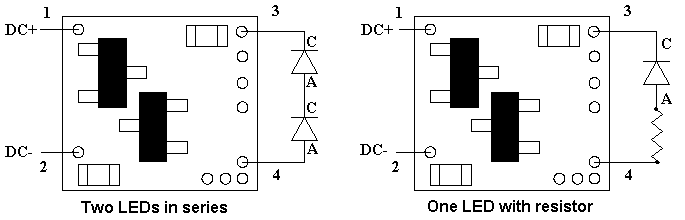
Figure 5
This completes connection of the N8047module. It is recommended that a thorough re-inspection of all connections and module placement be performed prior to applying power to the locomotive. We hope you enjoy the added realism our module provides.
© 2008 Ngineering